
Top 4 AI technologies: How to balance innovation and cybersecurity
Managed IT · Jun 24, 2025
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming businesses of all sizes, with small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) increasingly adopting these technologies to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences and strengthen their competitive advantage.
AI-powered technologies can offer significant benefits for SMBs, but they can also
introduce serious cybersecurity risks
, particularly when security configurations and default settings are not properly reviewed.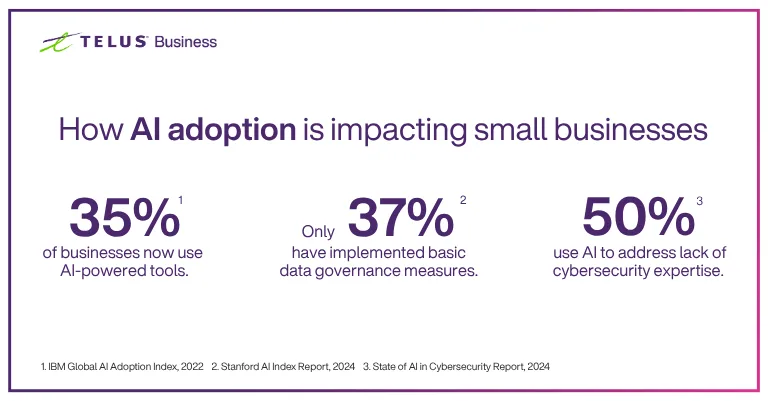
There are four most commonly used AI applications that can help SMBs, if employed with the
right cybersecurity plan
.1. Generative AI (Gen AI): OpenAI’s GPT models have revolutionized software development, data analysis, content creation, marketing, customer service, among other solutions. SMBs can use generative AI to produce written content, marketing materials and even software code. By automating tasks traditionally handled by professionals, generative AI has the potential to streamline workflows and make advanced capabilities more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
However, Gen AI can be a double-edged sword, as it can open the doors to new cyber threats to your business, such as:
- Phishing and social engineering: Generative AI models can produce highly realistic phishing emails that mimic corporate language and branding.Cybercriminals are creating tailored phishing messagesthat are harder for employees to detect, which can increase the risk of successful phishing attacks.
- Malware generation: Generative models can be trained to create malicious code snippets, which can be incorporated into larger malware programs. Cybercriminals could use this capability to automate malware development, making it easier for them to target and infiltrate businesses.
- Data privacy violations: When SMBs use generative AI for customer-facing applications, they may inadvertently expose private or sensitive data to third-party AI service providers. This can lead to data privacy issues if not carefully managed.
SMBs should invest in
employee training
on cybersecurity best practices, specifically focusing on phishing awareness and social engineering defence. Employing basic data protection steps, like removing personal information before using AI tools, may help keep sensitive data safe.2. AI-powered vision technology: This particular AI application leverages computer vision and machine learning to analyze images and videos, enabling tasks such as facial recognition, object detection and quality assurance. For SMBs in retail, healthcare and manufacturing, this technology can help to improve security through surveillance, enhance customer service with customer behaviour analyses and streamline operations by automating quality control processes.
While AI-powered vision technology can help bringing substantial benefits, it also introduces cybersecurity risks:
- Privacy concerns and data breaches: Vision-based AI systems may often collect extensive data, including video footage of employees and customers. If this data is not properly stored or not adequately secured, it can be a target for cyberattacks, leading to data breaches and significant privacy concerns.
- System vulnerabilities and unauthorized access: AI vision systems, such as smart cameras, are connected devices vulnerable to exploitation. A compromised camera can lead to unauthorized surveillance, allowing hackers to monitor a business or access other systems connected to the same network.
- Image spoofing and tampering: Hackers can manipulate or spoof images and videos to deceive AI vision systems, leading to inaccurate analyses or unauthorized access if the technology is used for identity verification.
To help mitigate the risks that can come from AI-powered vision technology, SMBs should implement strong data encryption for all stored and transmitted data. Conduct regular security audits of connected devices and network segmentation to help limit potential damage from a
breach
. Additionally, facial recognition and other sensitive applications should incorporate multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorized access
.3. Speech recognition and voice AI: AI technology can allow SMBs to automate customer service through voice-activated assistants, streamline internal processes with voice-activated systems and improve accessibility for employees and customers alike. SMBs are able to use voice AI to handle basic customer inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex interactions.
Although voice AI brings efficiencies, it could also expose SMBs to certain risks like:
- “Vishing”: This is a phishing voice tactic where attackers can use voice AI to mimic human voices. Cybercriminals may impersonate employees or executives to manipulate others into disclosing sensitive information.
- Unauthorized access through voice recognition: This is particularly dangerous for systems that grant access based on voice commands alone, as attackers can use voice recordings or synthesized voice patterns to gain unauthorized access.
- Data privacy and collection risks: Voice AI systems often record conversations for analysis, which can lead to privacy concerns if data storage practices are not secure. SMBs must help ensure that any recorded data is securely stored and protected from unauthorized access.
It’s imperative to enhance security protocols for voice recognition systems, possibly by combining them with other authentication methods like biometrics or passwords. Training employees on the risks of “vishing” and the importance of verifying sensitive requests through secondary channels can also help reduce the risk of voice-based social engineering attacks.
4. Deepfake technology:
Deepfakes
are media creations manipulated by an advanced artificial intelligence (AI), where images, voices, videos or text are digitally altered or fully generated by AI. While deepfake technology is often associated with negative use cases, it also holds potential for businesses in personalized employee training, marketing, content creation and more. The technology can use deepfake applications to create personalized video messages for customers or to produce cost-effective marketing content featuring virtual brand ambassadors. The concerning side of this technology is that it could bring significant threats in terms of cybersecurity:
- Impersonation and fraud: Cybercriminals can use deepfakes to impersonate business executives or employees in videos or audio messages, tricking other employees, customers, vendors or partners into disclosing sensitive information and authorizing fraudulent transactions.
- Brand reputation damage: Deepfake technology can be weaponized to create damaging content that falsely represents a company or its executives, which could lead to loss of customer trust and negative publicity.
- Verification challenges: As deepfakes become more convincing, businesses may struggle to verify the authenticity of video or audio content, increasing the risk of making decisions based on fraudulent information.
To help mitigate deepfake threats, SMBs can invest in tools that detect inauthentic content, including AI-based forensic solutions capable of identifying inconsistencies in videos or audio. Employee training is again a positive defence to help recognize signs of deepfake scams. Robust policies should also be in place to aid in verifying sensitive communications through multiple channels.
Take cybersecurity issues off your to-do list with TELUS Fully Managed
We help SMBs to better safeguard their data and operations from AI-driven threats by providing
comprehensive, tailored cybersecurity solutions for their specific needs.
With proactive monitoring, advanced threat detection and a dedicated team of specialists, we can help businesses like yours enhance cybersecurity around the clock. Our services include security tools that can help identify and mitigate threats in near real-time, improve employee training programs to counter social engineering and deliver strategic guidance to improve your overall cybersecurity posture. Connect with a managed IT specialist
today to learn how we can help take cybersecurity off your to-do list.Vivek Goyal is a product leader with over a decade of experience in cybersecurity, cloud and network. He has expertise in AI / ML, threat intelligence, risk management, compliance, frameworks, vulnerability management, and data security practices. He shares insights on the different aspects of the cybersecurity landscape, offering practical advice to help businesses succeed.
Authored by:
Vivek Goyal
Senior Technical Product Manager


